Test yourself: Should I get a hearing test?
Answer the 4 questions below to see if you should consider getting a hearing test.

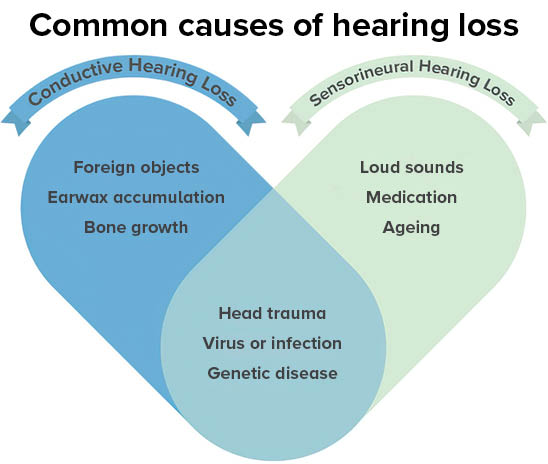
There are 3 overall types of hearing loss: Sensorineural, conductive, and mixed hearing loss. In treating hearing loss, it is important to understand the differences in order to determine the best treatment option.
The main types of hearing loss are differentiated based on which part of the ear is damaged:

Answer the 4 questions below to see if you should consider getting a hearing test.
Your answers indicate that you experience symptoms of hearing loss. We strongly recommend booking a hearing test in one of our clinics.
The result is an indication. An in-person hearing test can determine if you have a hearing loss.
Your answers indicate that you experience some symptoms of hearing loss. We recommend booking a hearing test in one of our clinics.
The result is an indication. An in-person hearing test can determine if you have a hearing loss.
Your answers do not indicate that you experience symptoms of hearing loss. However, if you experience trouble hearing, we recommend booking a hearing test in one of our clinics.
The result is an indication. An in-person hearing test can determine if you have a hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. When experiencing sensorineural hearing loss, sounds may be unclear or difficult to hear. Voices in conversation may be distorted, and it may seem like others are mumbling.
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss
The natural ageing process (age-related hearing loss / presbycusis)
Excessive exposure to noise (noise-induced hearing loss).
Treating sensorineural hearing loss
This type of hearing loss is often treated with hearing aids.

Conductive hearing loss is usually a result of a disruption to the sound's path as it travels from the outer / middle ear to the inner ear.
Causes of conductive hearing loss
This type of hearing loss can also be caused by an obstruction in the ear canal, such as earwax or liquid preventing sound from reaching the ear drum.
Treating conductive hearing loss
Treatment for conductive hearing loss includes: earwax removal, medical treatments, and surgical treatments.

"It's not something that you notice immediately, it creeps up on you. I got really annoyed when people shouted at me. I can now hear the cat purr and the clock behind me, these are my little gems"
There are other ways to describe hearing loss types. For example:
- High or low-frequency: Indicates whether you are unable to hear high or low-pitched sounds (i.e. high frequency hearing loss means you cannot hear high-pitched sounds)
High frequency hearing loss
Low frequency hearing loss
- Unilateral or bilateral: Indicates whether one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) ears are affected by hearing loss
Bilateral hearing loss
Unilateral hearing loss
- Progressive or sudden hearing loss: Indicates whether the hearing loss happens quickly or gradually over time
- Acquired or congenital: Indicates whether your hearing was present at birth or acquired at a later stage in life


Tinnitus is a ringing, buzzing, whistling, roaring, or hissing sound in the ear that only you can hear. Tinnitus affects 15-20% of people, and it is very often one of the first signs of hearing loss.
The most common cause is exposure to excessive noise, which damages the tiny hair cells in the inner ear. The sound of tinnitus is the result of your brain trying to compensate for the loss of hair cells. The brain misinterprets the reduced signals from the ear, resulting in a perception of sound, or tinnitus.
1. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tinnitus/symptoms-causes
2. David M Baguley, Mechanisms of tinnitus, British Medical Bulletin, Volume 63, Issue 1, October 2002, Pages 195–212, https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/63.1.195
3. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/hearing-aids/hearing-loss
4. https://hearinghealthfoundation.org/types-of-hearing-loss
5. https://www.ishaa.ie/hearing/
6. https://pathsocjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/path.2102